
External-DNS - Automated DNS Management for k3s Homelab
Pre-requisites
- k3s installed and running
- kubectl
- Access to a supported DNS provider (e.g., Cloudflare, Pi-hole, or other supported providers)
- helm (optional, for Helm installation method)
- fluxcd (optional, for GitOps installation method)
- sops (optional, for secret management)
Are you tired of manually managing DNS records for your homelab services? This guide will walk you through implementing automated DNS management using External-DNS, a powerful tool that automatically creates and manages DNS records for your Kubernetes services.
Let’s explore how to set up External-DNS in a k3s homelab environment, focusing on common DNS providers used in homelab setups.
How I did it in nutshell?
I’m using FluxCD to manage my k3s cluster and I’m installing External-DNS through FluxCD. Moreover I’m using Cloudflare as my DNS provider and I’m using a secret (SOPS) to store my Cloudflare API key. That’s it you could do it in a different way, but this is the pragmatic way to do it in my opinion.
Let’s start do it
Step 1: Choose and Configure DNS Provider
- Select Provider: Choose your DNS provider (we’ll use Cloudflare as an example)
- API Access: Generate necessary API tokens/keys for your DNS provider
- Domain Preparation: Ensure your domain is configured in your DNS provider
Step 2: Install External-DNS, I’m installing it through GitOps FluxCD
Keep in mind that secret is unecrypted via FluxCD. FluxCD has global sops key and it’s used to decrypt all secrets in the cluster.
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Kustomization
resources:
- namespace.yaml
- cloudflare.secret.sops.yaml
- external-dns.yaml---
apiVersion: source.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1beta1
kind: HelmRepository
metadata:
name: external-dns
namespace: external-dns
spec:
interval: 1h
url: https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/external-dns/
---
apiVersion: helm.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v2beta1
kind: HelmRelease
metadata:
name: external-dns
namespace: external-dns
spec:
interval: 1m
chart:
spec:
chart: external-dns
version: ">=1.13.0"
sourceRef:
kind: HelmRepository
name: external-dns
namespace: external-dns
interval: 1m
values:
provider: cloudflare
env:
- name: CF_API_TOKEN
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: cloudflare-api-key
key: apiKeyKeep in mind that you need to create a secret with your Cloudflare API key. I’m using SOPS to encrypt my secret and it’s available in my GitHub repository.
Check if kustomization is applied and resources are created
Kustomization part of the repository is applied and resources are created.
~/Projects/homenavi main X φ flux get kustomizations -n flux-system
NAME REVISION SUSPENDED READY MESSAGE
external-dns main/e183a35 False True Applied revision: main/e183a35
flux-system main/e183a35 False True Applied revision: main/e183a35 Pods are running and secret has been created.
~/Projects/homenavi main X φ k get po -n external-dns
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
external-dns-6664d4875d-p6bfm 1/1 Running 0 76s
~/Projects/homenavi main X φ k get secret -n external-dns
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
cloudflare-api-key Opaque 1 16m
sh.helm.release.v1.external-dns.v1 helm.sh/release.v1 1 16mWe have everything we need to start testing. Let’s create a new simple nginx server and check if External-DNS will create a new DNS record.
I prepared test yaml file to create a new nginx server.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx
name: nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx
spec:
selector:
app: nginx
type: LoadBalancer
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: nginx-app
annotations:
external-dns.alpha.kubernetes.io/hostname: testowy.devkblaz.com
external-dns.alpha.kubernetes.io/ttl: "120"
external-dns.alpha.kubernetes.io/cloudflare-proxied: "true"
external-dns.alpha.kubernetes.io/target: "144.24.170.30"
spec:
rules:
- host: testowy.devkblaz.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: nginx
port:
number: 80Explanation of the file:
- Deployment and Service are creating a new nginx server
- Ingress is creating a new DNS record for the nginx server
- External-DNS annotation target this is Public IP of my node
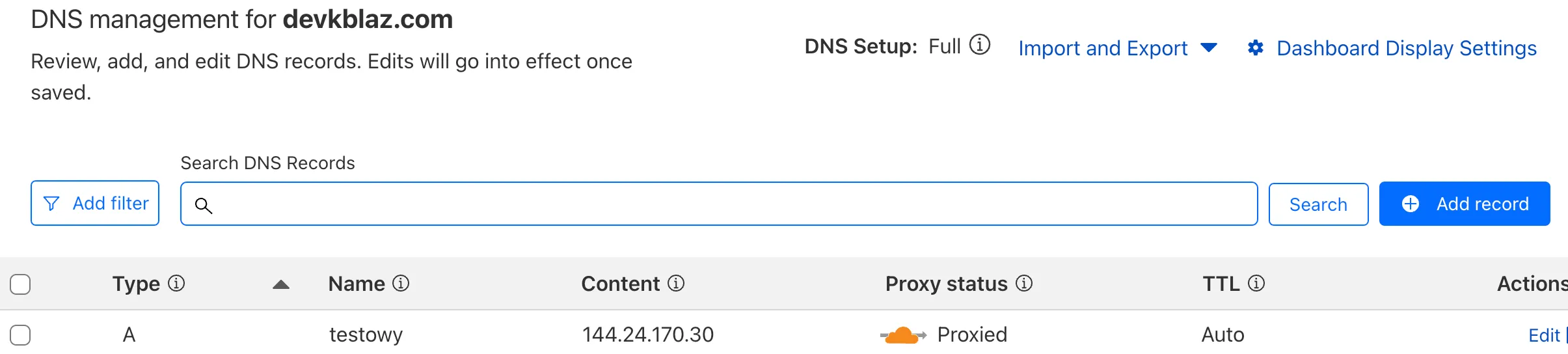
Check if DNS record is created on Cloudflare side
First check logs of External-DNS pod.
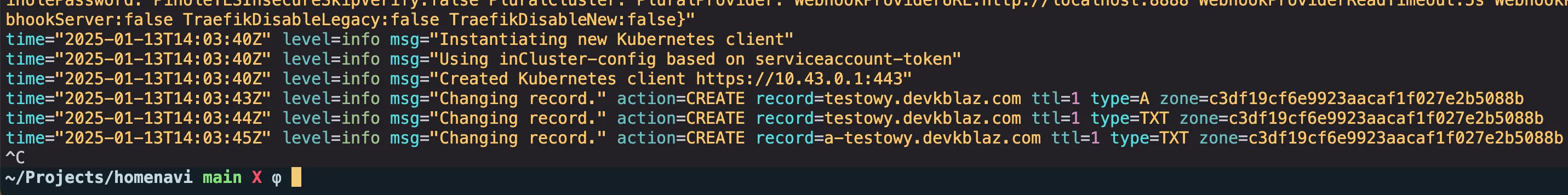 It looks like External-DNS is working and it’s creating a new DNS record.
It looks like External-DNS is working and it’s creating a new DNS record.
Let’s confirm that DNS record is created on Cloudflare side.
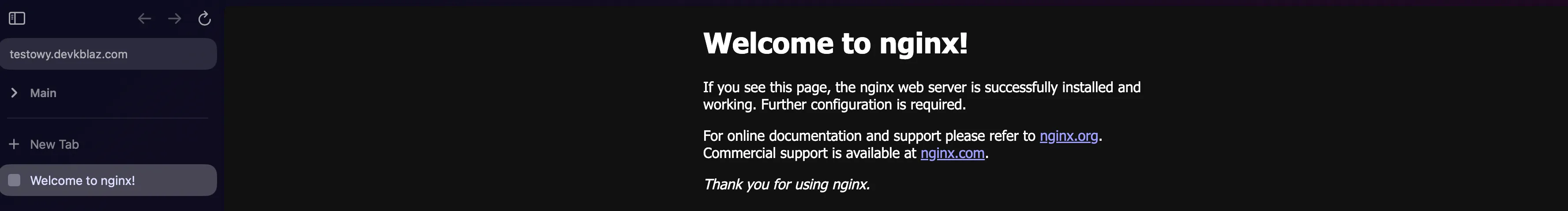
Let’s check if nginx is working.
Summary
External-DNS provides a robust solution for automating DNS management in your k3s homelab environment. By implementing this setup:
- You eliminate manual DNS record management
- Achieve consistent and automated DNS updates
- Integrate seamlessly with popular DNS providers
- Maintain GitOps practices with FluxCD
- Secure sensitive information using SOPS encryption
Related Posts
VolSync - Kubernetes Volume Replication Made Simple
Implement asynchronous volume replication for Kubernetes using VolSync with MySQL database synchronization.
Velero - Kubernetes Backup and Restore Made Simple
Master Kubernetes cluster backups, disaster recovery, and data migration with Velero in your Azure Kubernetes infrastructure.